Decentralized finance, or DeFi has experienced rapid and transformative growth in recent years. This has disrupted traditional financial systems and introduced innovative solutions.
Yield farming and liquidity pools, two fundamental innovations that fueled DeFi’s rise, have transformed how we think about lending, borrowing, and trading digital assets.
Rise of Yield Farming
Yield farming, known as liquidity mining, arose as an innovative technique to motivate users to provide liquidity to DeFi protocols. Users who deposit cryptocurrency into lending or liquidity pools can earn incentives through newly minted tokens or a portion of the protocol’s transaction fees.
This incentive system has proven to be an effective instrument. It helps attract liquidity, which is critical to the smooth operation and adoption of DeFi platforms.
However, yield farming is not without obstacles. The huge benefits associated with yield farming have frequently resulted in the establishment of unsustainable economic models. Moreover, the protocols are heavily reliant on token inflation to attract liquidity.
Furthermore, the frequent migration of cash between various yield farming prospects has resulted in significant volatility and instability.
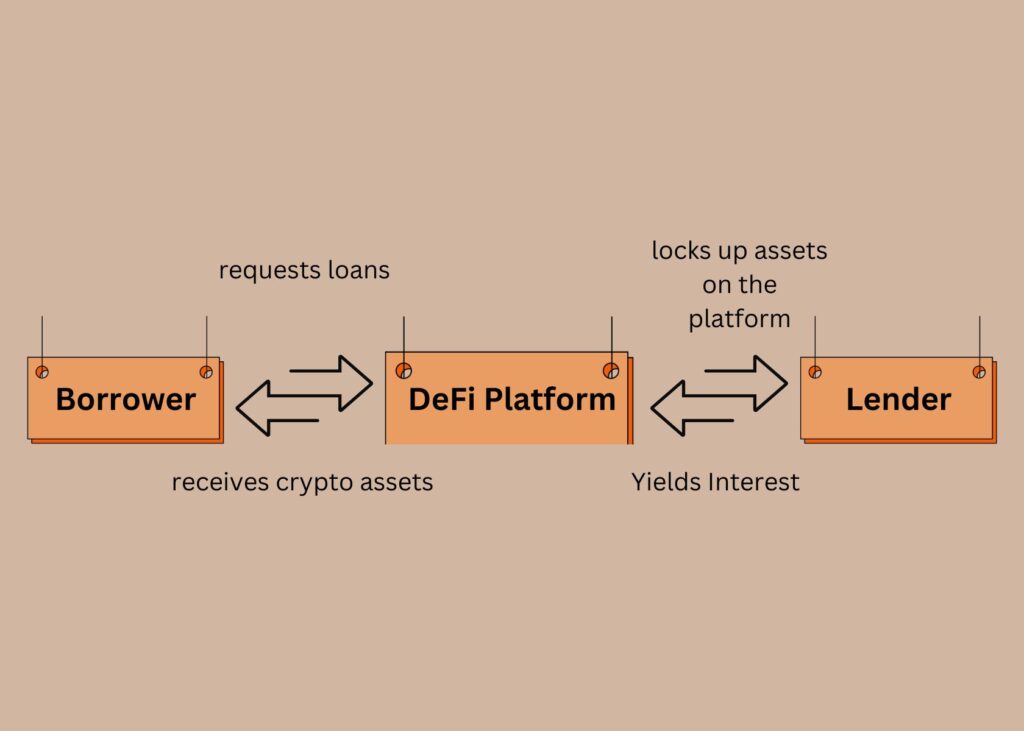
Liquidity Pools and Automated Market Makers
Another significant development in DeFi has been the establishment of liquidity pools and automated market makers (AMMs). These decentralized exchanges (DEXs) have transformed how digital assets are exchanged. They have eliminated the need for centralized order books and market makers.
Liquidity pools are crowdsourced pools of digital assets used for trading on DEXs. Users can deposit tokens into these pools and get a portion of the trading fees produced.
In contrast, AMMs employ mathematical algorithms to automatically compute asset prices based on the liquidity pool’s asset ratio.
There are numerous advantages to liquidity pools and AMMs. They promote decentralization, ensure constant liquidity, and allow frictionless trade without intermediaries.
However, these innovations confront impermanent loss (the danger that liquidity providers would suffer losses due to the volatility of the assets in the pool) and the possibility of price manipulation in smaller pools.
Emerging DeFi Innovations
Although yield farming and liquidity pools have paved the way for DeFi’s expansion, the ecosystem constantly evolves, resulting in new and interesting developments.
Perpetual contracts and decentralized derivatives
One area that has seen substantial growth is the development of decentralized derivatives and perpetual contracts. These financial products allow users to bet on the price swings of various assets without actually owning them, providing new potential for hedging and trading techniques.
Undercollateralized lending protocols
Undercollateralized lending procedures are yet another novel area in DeFi. Unlike traditional lending platforms, which require customers to overcollateralize their loans, these protocols use alternative trustworthiness indicators, such as social collateral or credit score algorithms.
This strategy could increase access to credit and financial services for persons and businesses who were previously excluded.
Programmable money and conditional transactions
Programmable money and conditional transactions are also becoming effective tools in the DeFi ecosystem. These characteristics allow for the establishment of smart contracts that can automatically perform transactions depending on predefined criteria, paving the stage for more complicated financial applications and automation.
DAO governance and decentralized decision-making
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) and decentralized decision-making processes are gaining popularity as ways to control DeFi protocols and ensure community participation in decision-making.
This method encourages transparency and accountability while aligning stakeholders’ interests with the long-term success of the procedures.
NFT financialization and fractional ownership
Another example of innovation is the financialization of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and fractional ownership. DeFi protocols enable new investment and ownership by tokenizing real-world assets or digital artifacts. This makes previously illiquid assets more accessible to a larger market.
Conclusion
As the DeFi ecosystem evolves and innovates, it becomes evident that yield farming and liquidity pools were only the beginning.
The rise of decentralized derivatives, undercollateralized lending protocols, programmable money, DAO governance, and NFT financialization are pushing the limits of DeFi.
However, responsible innovation and collaboration will be critical to these breakthroughs’ long-term viability and acceptance.
By tackling issues like legal uncertainty, security risks, scalability, and user experience limitations, the DeFi ecosystem can continue transforming the financial environment and opening new avenues for financial inclusion, transparency, and democratization.
The future of DeFi is bright, and emerging ideas can transform how we think about money, giving individuals and communities greater control over their financial lives.



